This ultimate guide will take you through everything you need to know about GA4, from its core philosophy to advanced features, ensuring you are fully equipped to leverage its power.
1. What is Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Why the Shift?
GA4 is Google’s latest generation of analytics that operates on an event-based data model, a fundamental departure from Universal Analytics’ session-based model. This shift was driven by several key factors:
Cross-Platform Tracking: In today’s multi-device world, users interact with businesses across websites and mobile apps. GA4 is designed to track user journeys seamlessly across these different platforms, providing a holistic view of the customer.
Privacy-Centric Design: With increasing global privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA), GA4 was built with privacy in mind, offering more granular controls over data collection and supporting a future with less reliance on cookies.
Machine Learning Capabilities: GA4 leverages Google’s advanced machine learning to provide predictive metrics and insights, helping marketers anticipate future user behavior (e.g., churn probability, purchase probability).
Enhanced Reporting Flexibility: While UA offered fixed reports, GA4 provides more customizable exploration tools, allowing analysts to build bespoke reports to answer specific business questions.
Key Difference:
Universal Analytics (UA): Session-based model. Data revolves around « sessions » and « pageviews. »
Google Analytics 4 (GA4): Event-based model. Every interaction (page view, click, scroll, purchase) is treated as an « event. » This offers much more flexibility and detail.
2. Setting Up Your GA4 Property: A Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up GA4 correctly is crucial for accurate data collection. We assume you already have Google Tag Manager (GTM) installed, as it’s the recommended method for GA4 implementation.
2.1. Creating a New GA4 Property
Access Google Analytics: Go to analytics.google.com.
Navigate to Admin: Click on
Admin(the gear icon) in the bottom-left corner.Create Property: In the « Property » column, click
Create Property.Property Details:
Property Name: Give your property a clear name (e.g.,
YourCompanyName - GA4).Reporting Time Zone: Select your business’s time zone.
Currency: Select your primary currency.
Click
Next.
Business Information:
Select your industry category and business size.
Choose your business objectives (e.g., « Generate leads, » « Drive online sales »). This helps GA4 tailor initial reports.
Click
Create.
2.2. Setting Up a Data Stream (Web)
After creating the property, you’ll be prompted to choose a platform for data collection.
Choose a Platform: Select
Web.Website URL: Enter your website’s URL (e.g.,
https://www.yourwebsite.com).Stream Name: Give your stream a name (e.g.,
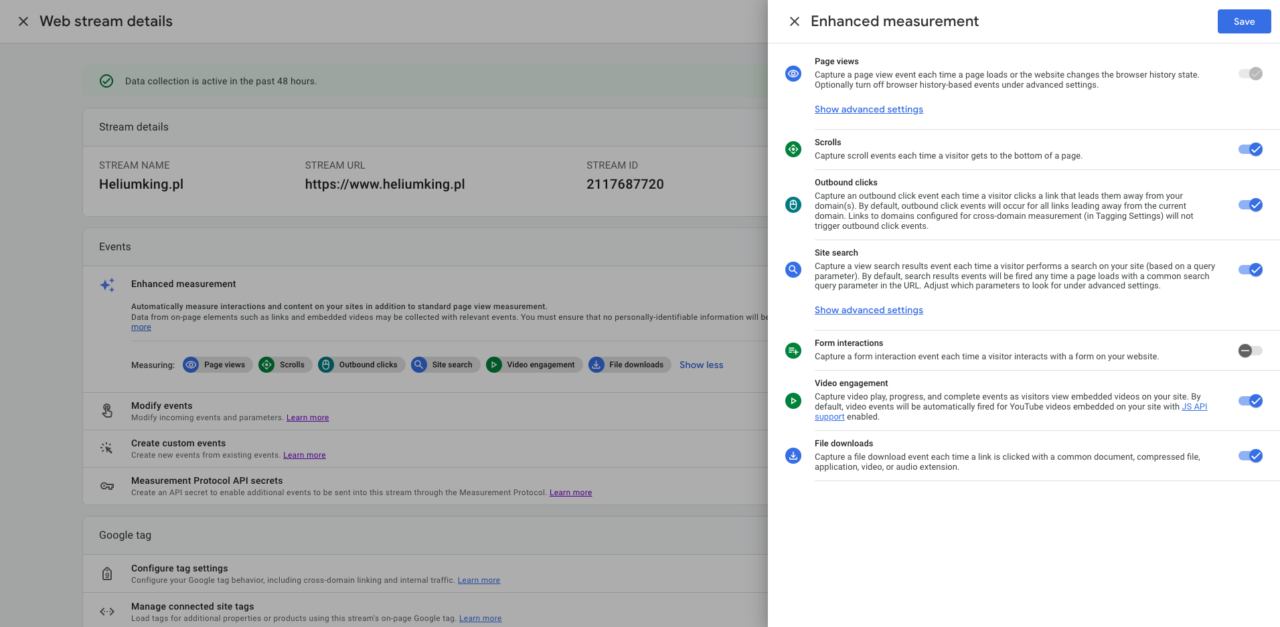
YourWebsite - Web Stream).Enhanced Measurement: Ensure « Enhanced measurement » is turned on. This automatically tracks common events like page views, scrolls, outbound clicks, site search, video engagement, and file downloads without additional tag configuration.
- Get Measurement ID: After creation, you’ll see your Measurement ID (starts with
G-XXXXXXXXX). Copy this ID; you’ll need it for GTM.
2.3. Implementing GA4 via Google Tag Manager (GTM)
Open Google Tag Manager: Go to tagmanager.google.com and select your website’s container.
Create a New Tag: Click
New Tag.Tag Configuration:
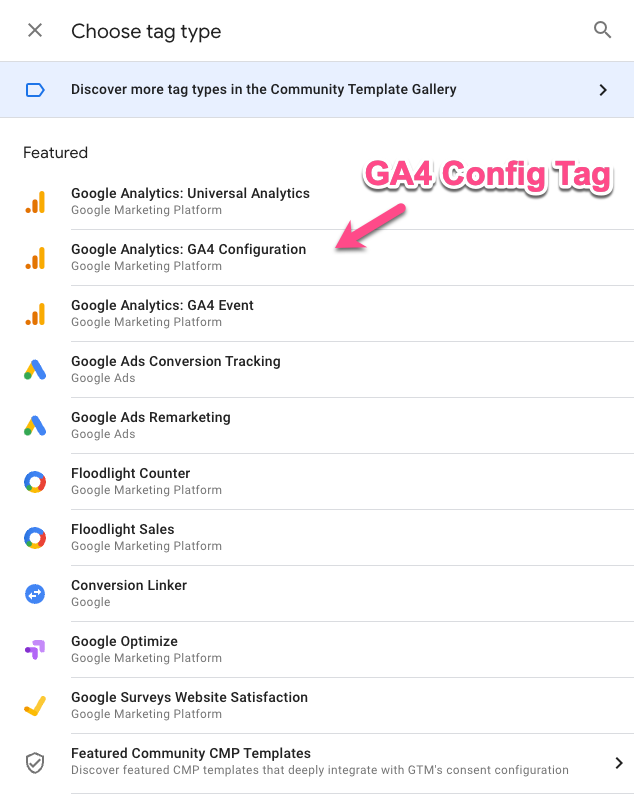
Click on « Tag Configuration » and choose
Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration.
Measurement ID: Paste the Measurement ID (
G-XXXXXXXXX) you copied from GA4 into the « Measurement ID » field.Triggering: Click on « Triggering » and select
All Pages. This ensures your GA4 configuration tag fires on every page load.Name and Save: Give your tag a descriptive name (e.g.,
GA4 - Base Configuration) and clickSave.Submit and Publish: Crucially, click the
Submitbutton in the top right corner of GTM to publish your changes live to your website. Add a version name (e.g., « GA4 Base Setup ») and a description.
3. Key Concepts and Features in GA4: Understanding the Event-Driven World
To effectively use GA4, it’s essential to grasp its core concepts:
3.1. Events: The Core of GA4
Everything in GA4 is an event. There are four categories of events:
Automatically collected events: These are collected by default when you install GA4 (e.g.,
page_view,scroll,click).Enhanced measurement events: These are automatically collected if « Enhanced measurement » is enabled (e.g.,
file_download,video_start,view_search_results).Recommended events: Google suggests these for common use cases, but you need to implement them (e.g.,
login,purchase,add_to_cart). They have predefined names and parameters.Custom events: Any other event you define to collect data specific to your business needs (e.g.,
form_submission_success,cta_button_click).
3.2. Parameters: Adding Context to Events
Events often come with parameters, which provide additional context. For example, a page_view event might have parameters like page_location (URL) and page_title. A purchase event could have transaction_id, value, currency, and items (an array of product details).
3.3. Users and User Engagement
GA4 focuses heavily on user behavior. It uses multiple identifiers (User-ID, Google signals, device ID) to de-duplicate users across platforms and devices, aiming for a more accurate understanding of individual user journeys.
Engaged Sessions: A session that lasts longer than 10 seconds, or has a conversion event, or has 2 or more page/screen views. This is a key metric for understanding quality traffic.
Engagement Rate: The percentage of engaged sessions.
Life Cycle Reporting: GA4 reports are structured around the user lifecycle (Acquisition, Engagement, Monetization, Retention).
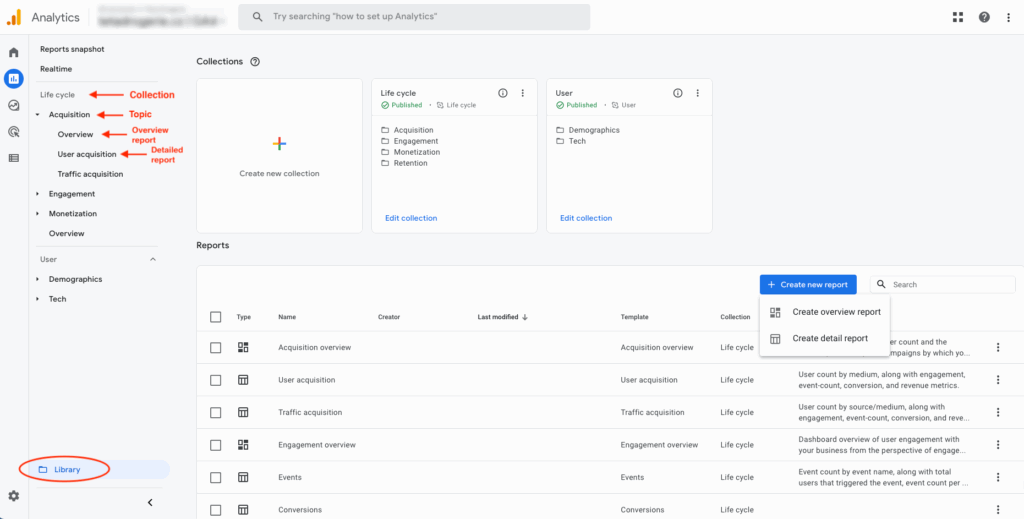
4. Navigating GA4 Reports and Explorations
The « Reports » section provides pre-built reports organized by the user lifecycle:
Reports Snapshot: A customizable dashboard offering a quick overview of key metrics.
Realtime: See what’s happening on your site/app right now.
Acquisition: How users find your site (traffic sources, campaigns).
Engagement: How users interact with your content (events, pages, scrolls).
Monetization: Performance of your e-commerce or monetization efforts.
Retention: How well you retain users over time.
Demographics / Tech: Insights into your audience.
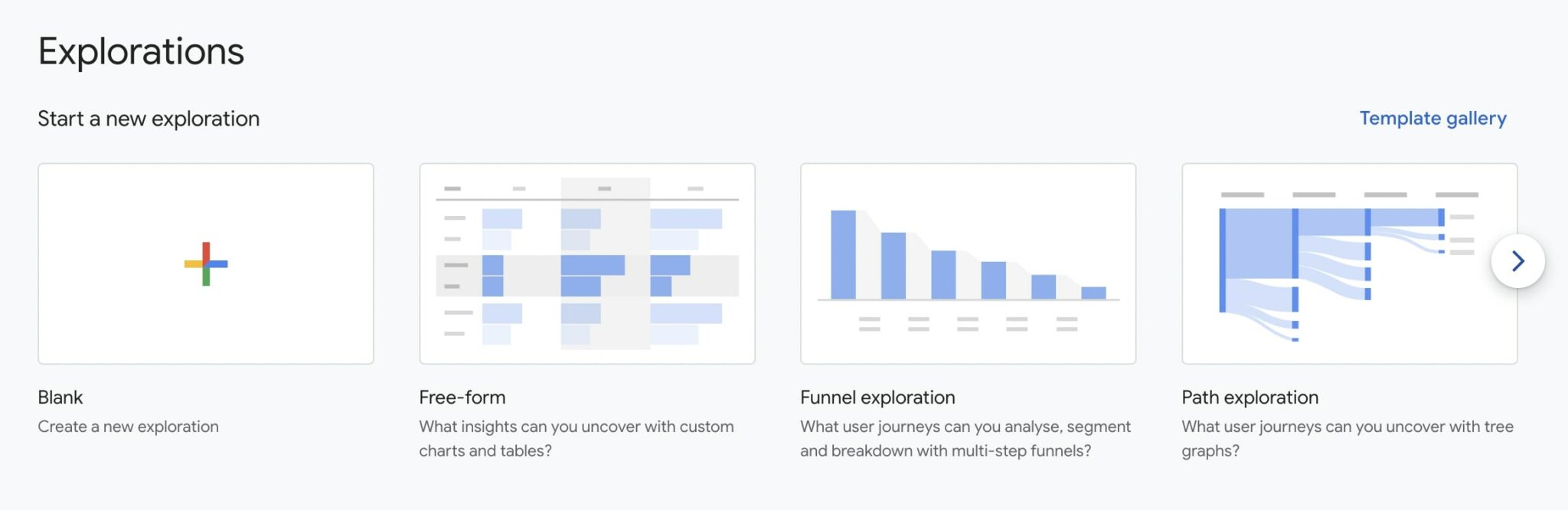
4.2. Explorations: Advanced Reporting and Analysis
This is where GA4 truly shines for analysts. The « Explore » section allows you to build custom reports using powerful techniques:
Free-form: Drag-and-drop dimensions and metrics to create pivot tables, bar charts, line charts, etc.
Funnel exploration: Visualize the steps users take to complete a conversion, identify drop-off points.
Path exploration: See the actual paths users take through your site/app (forward and backward).
Segment overlap: Understand how different user segments overlap.
User explorer: Dive deep into the activity of individual (anonymized) users.
Cohort exploration: Analyze the behavior of groups of users who share a common characteristic.
User lifetime: Understand the lifetime value of your users
These tools empower you to answer complex business questions that were difficult or impossible in UA.
5. Key Benefits of Using GA4: Unlock Your Data Potential
Adopting GA4 brings a multitude of benefits for your digital strategy:
Unified Customer View: Seamlessly track users across websites and apps, providing a truly holistic understanding of their journey.
Enhanced Event Tracking: Granular data collection allows for more precise insights into user behavior and interactions.
Future-Proof Analytics: Built to adapt to a privacy-first, cookieless future, ensuring your data collection remains robust.
Predictive Capabilities: Machine learning-powered insights help you anticipate future trends and user actions.
Flexible Reporting: Customize reports to precisely answer your business questions and uncover deeper insights.
Improved ROI Measurement: Better data leads to better optimization, translating into more effective marketing campaigns and higher ROI.
Deeper Engagement Metrics: Focus on « engaged sessions » provides a more meaningful understanding of user quality compared to simple bounce rate.
Conclusion: Embrace the Future of Analytics with GA4
Google Analytics 4 is more than just an update; it’s a paradigm shift in how we collect, process, and understand digital data. Its event-based model, privacy-centric design, and powerful exploration tools position it as the essential analytics platform for any business operating in the complex and dynamic digital landscape of 2025.
While there’s a learning curve from Universal Analytics, the benefits of embracing GA4 far outweigh the initial effort. By transitioning now, you’re not just ensuring business continuity; you’re unlocking a new level of data mastery that will empower you to make smarter decisions, optimize your marketing efforts, and drive sustainable growth.

